Can AI Search Bots Crawl My Website? A Technical Guide for Marketers

GPTBot just jumped from #9 to #3 in global crawler traffic rankings. PerplexityBot requests surged by 157,490%.
Somewhere in your server logs, AI crawlers are hitting your pages thousands of times per day—whether you realize it or not.
For B2B marketing leaders watching organic traffic decline while CAC climbs, the question “Which bots crawl my website?” has shifted from technical housekeeping to a strategic imperative. AI platforms like ChatGPT now drive 87% of AI referral traffic, and that traffic converts with significantly lower bounce rates than traditional organic visitors.
This guide breaks down exactly which AI bots are accessing your site, why they fail to read JavaScript, and how to configure access for maximum visibility in AI-generated answers.
What Are AI Search Bots and How Do They Differ from Googlebot?
AI search bots are web crawlers that collect data for large language models (LLMs) rather than traditional search indexes. While Googlebot indexes your pages to determine search rankings, AI crawlers gather content to train models and power real-time AI responses.
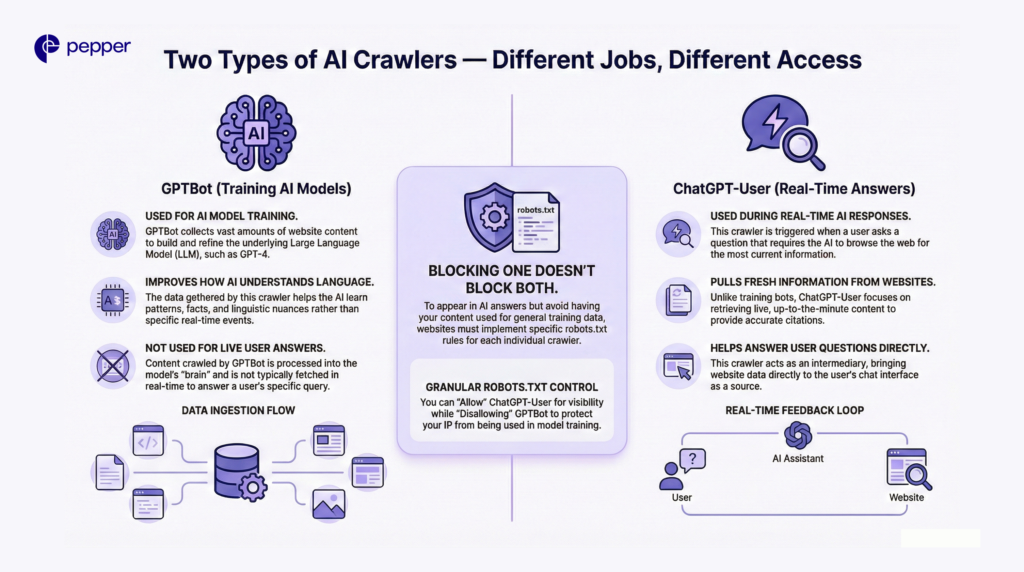
The Two Types of AI Crawlers
It is critical to distinguish between the two types of bots that OpenAI and others operate. Blocking one does not necessarily block the other.
- Training Crawlers (e.g., GPTBot): Scrapes vast amounts of data to train future models (like GPT-5).
- Live-Retrieval Crawlers (e.g., ChatGPT-User): Fetches live data when a user asks a specific question requiring up-to-date info.
Why This Matters: If you want your content to appear in ChatGPT’s real-time answers (branding) but don’t want your IP used to train their model (copyright), you need granular robots.txt rules.
Feature Comparison: Googlebot vs. AL Bots
| Factor | Traditional (Googlebot) | AI Crawlers (GPTBot, ClaudeBot) |
| Primary Purpose | Index for Search Rankings | Train LLMs / Power AI Answers |
| JS Rendering | ✅ Renders fully | ❌ Cannot execute JavaScript |
| Crawl-to-Referral | 3:1 to 30:1 | Up to 100,000:1 (High cost, low traffic) |
| Robots.txt | Strict Compliance | Mostly respectful, some ignore |
| Ranking Impact | Direct SEO Impact | No direct SEO impact (currently) |
Which AI Bots Are Currently Crawling Websites?
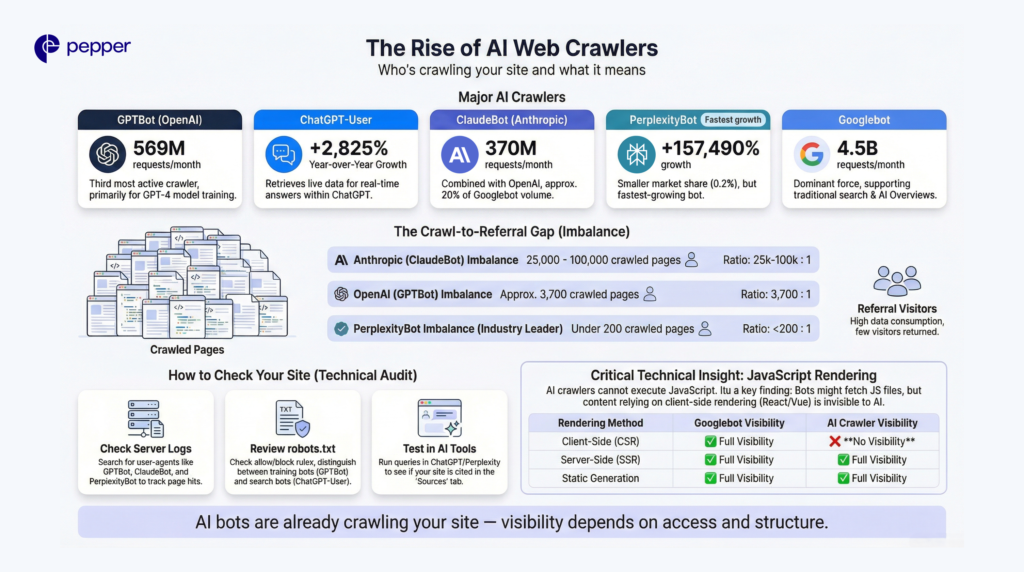
The AI crawler landscape has exploded over the past 18 months. According to Cloudflare data from July 2025, here are the major players you need to identify in your logs.
- OpenAI Crawlers: GPTBot generated 569 million requests across Vercel’s network in a single month. ChatGPT-User requests surged 2,825% year-over-year.
- Anthropic Crawlers: ClaudeBot follows with 370 million monthly requests. Combined with GPTBot, these represent about 20% of Googlebot’s 4.5 billion monthly requests.
- Perplexity Crawlers: PerplexityBot maintains only 0.2% market share but recorded the highest growth rate at 157,490% increase in raw requests.
- Google AI Crawlers: Googlebot’s share rose from 30% to 50%, potentially supporting both traditional search indexing and AI Overviews functionality.
The Crawl-to-Referral Imbalance
Here’s where AI crawlers get problematic for publishers. For every visitor Anthropic refers back to websites, its crawlers have already visited tens of thousands of pages.
Anthropic’s ratios range from 25,000:1 to 100,000:1—meaning massive data collection with minimal return traffic. OpenAI’s ratios reached 3,700:1. Perplexity maintains the lowest ratios at under 200:1, making it the most publisher-friendly AI crawler.
✓ AI Crawler Identification Checklist
- Review server logs for GPTBot, ClaudeBot, and PerplexityBot user agents
- Check robots.txt for existing AI-specific directives
- Monitor crawl frequency trends over the past 6 months
- Document crawl-to-referral ratios for each AI platform
- Identify which crawlers respect vs ignore your current rules
How to Check If AI Bots Are Accessing Your Site
Before optimizing, you need a baseline. Here are three ways to audit your current AI exposure.
1. Server Log Analysis
Your server logs contain “User Agent” strings that identify visitors. Ask your dev team to grep your logs for these specific identifiers:
GPTBotChatGPT-UserClaudeBotPerplexityBotGoogle-Extended
2. Robots.txt Review
Check yourdomain.com/robots.txt. If you do not see specific directives for the bots listed above, they likely have full access to your public content.
3. Real-Time Verification (The “Ego Search”)
Test your visibility manually. Open ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Gemini. Ask questions that should trigger your content.
- Check: Does the answer contain your information?
- Check: Does Perplexity list you in the “Sources” tab?
- Solution: If you have quality content but aren’t appearing, the issue is likely Technical Access or Content Structure.
Pro Tip: Tools like Pepper’s Atlas platform automate this. Atlas tracks brand mentions across ChatGPT, Gemini, and Perplexity daily, turning manual checking into continuous Share-of-Voice data.
Why JavaScript Rendering Matters for AI Crawlability
Here’s a technical barrier that trips up many marketing teams: AI crawlers cannot execute JavaScript.
Vercel research confirms that none of the major AI crawlers currently render JavaScript. While ChatGPT and Claude crawlers fetch JavaScript files (11.5% and 23.84% of requests, respectively), they don’t execute them. Any content rendered client-side remains invisible to AI bots.
What This Means for Your Content
If your website relies on JavaScript frameworks like React or Vue without server-side rendering, AI crawlers see blank pages or incomplete content. Your blog posts, product pages, and documentation might rank well in Google (which renders JavaScript) while remaining completely invisible to ChatGPT and Perplexity.
Server-Side Rendering Solutions
Prioritize server-side rendering for all critical content. This includes:
- Main content (articles, product information, documentation)
- Meta information (titles, descriptions, categories)
- Navigation structures
Frameworks like Next.js and Nuxt.js support SSR by default. Static site generation (SSG) and incremental static regeneration (ISR) also keep content accessible to all crawlers.
| Rendering Method | Googlebot Visibility | AI Crawler Visibility |
|---|---|---|
| Client-Side (CSR) | ✓ Full | ✗ None |
| Server-Side (SSR) | ✓ Full | ✓ Full |
| Static Generation | ✓ Full | ✓ Full |
| Hybrid (ISR) | ✓ Full | ✓ Full |
Key Takeaway: JavaScript rendering is the single biggest technical barrier to AI visibility. If your content relies on client-side rendering, AI crawlers can’t see it—regardless of how well you rank in traditional search.
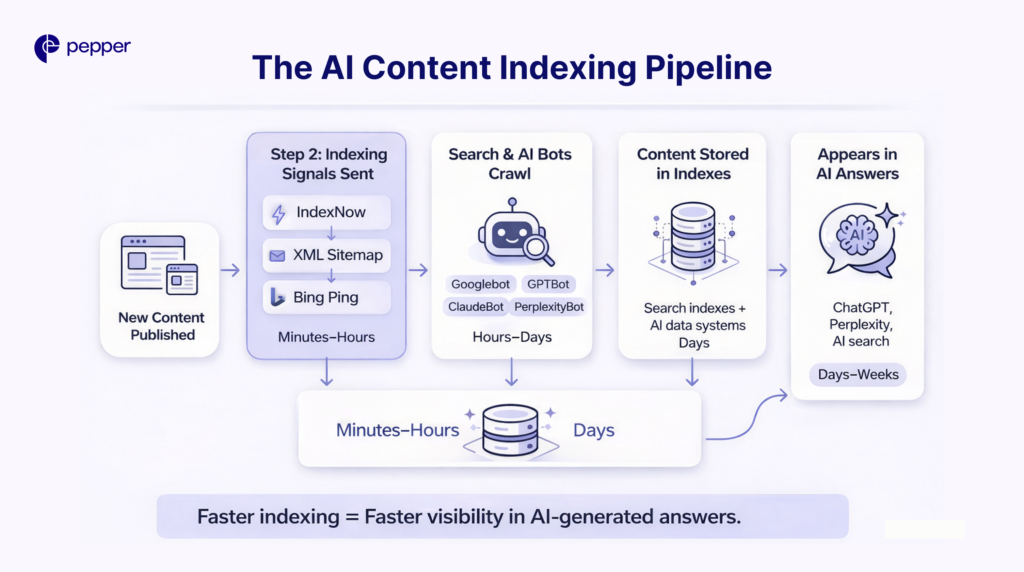
How to Get Google and AI Bots to Crawl Your Website Faster
Speed matters for AI visibility. The faster crawlers index new content, the sooner it appears in AI-generated responses.
Implement IndexNow Protocol
IndexNow reduces indexing time from days to minutes by proactively alerting search engines when content changes. By late 2023, over 60 million websites were using IndexNow to publish 1.4 billion URLs daily.
One caveat: Google hasn’t joined the IndexNow protocol. It primarily benefits Bing and Yandex visibility—but since many AI platforms pull from multiple sources, faster Bing indexing often improves AI discoverability.
Optimize Your XML Sitemap
Submit updated sitemaps after publishing new content. Include priority tags for high-value pages. Remove outdated or thin content that wastes crawl budget.
Push Content Directly
Sitemaps, IndexNow alerts, and direct Bing submissions all proactively signal new content availability. This encourages AI bots to prioritize your fresh content over competitors’ older pages.
✓ Crawl Acceleration Checklist
- Implement IndexNow protocol for instant Bing notification
- Update XML sitemap within 24 hours of new content
- Submit sitemap directly to Bing Webmaster Tools
- Remove thin or outdated content wasting crawl budget
- Monitor crawl frequency changes in server logs
Should You Block or Allow AI Crawlers?
This decision depends entirely on your business model and content strategy. Both approaches carry significant trade-offs.
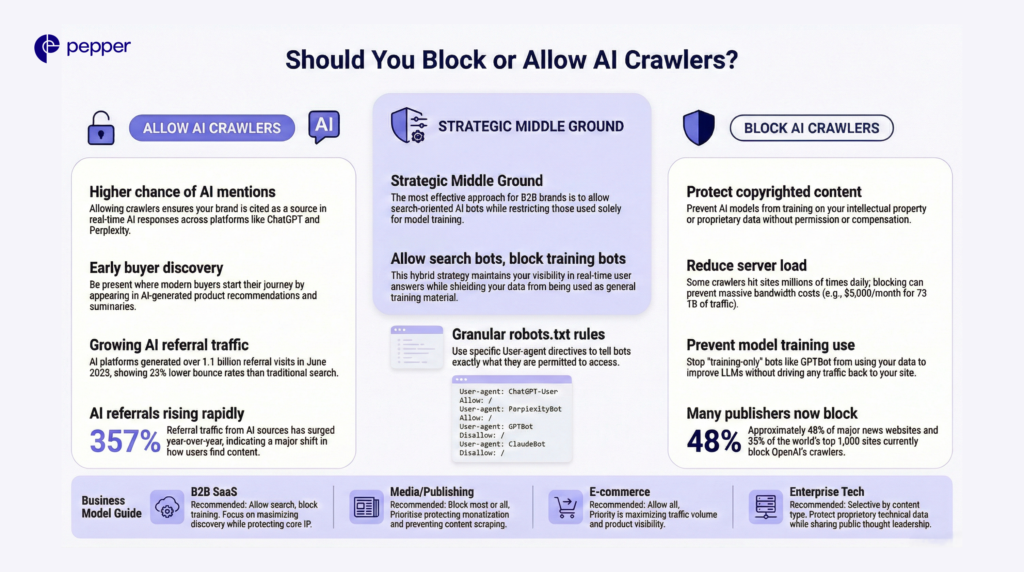
The Case for Allowing AI Crawlers
Allowing trusted LLMs and search bots increases your chances of being cited in ChatGPT responses, selected as a Perplexity source, and discovered early in buyer journeys. AI platforms generated over 1.1 billion referral visits in June 2025—up 357% year-over-year.
That traffic quality matters too. AI referral visits show 23% lower bounce rates, 12% more page views, and 41% longer sessions than non-AI traffic.
The Case for Blocking AI Crawlers
Media companies and publishers concerned with copyright, content reuse, or monetization often choose blocking. By the end of 2023, 48% of major news websites blocked OpenAI’s crawlers. Over 35% of the world’s top 1,000 websites now block GPTBot.
Some sites face resource concerns. Repair guide iFixit reported Anthropic’s crawlers hit their website nearly a million times in one day. Read the Docs documented 73 TB of crawler access in May alone, costing $5,000 in bandwidth.
Strategic Middle Ground
The most effective approach for B2B brands: allow AI search crawlers while blocking training-only crawlers.
# Allow AI search features
User-agent: ChatGPT-User
Allow: /
User-agent: PerplexityBot
Allow: /
# Block training crawlers
User-agent: GPTBot
Disallow: /
User-agent: ClaudeBot
Disallow: /
This configuration maintains visibility in AI-powered search results while protecting content from training datasets. Pepper’s GEO methodology incorporates this strategic crawler management as part of comprehensive AI visibility optimization—balancing content protection with discovery opportunity.
| Business Model | Recommended Approach | Rationale |
|---|---|---|
| B2B SaaS | Allow search, block training | Maximize discovery, protect IP |
| Media/Publishing | Block most or all | Protect monetization |
| E-commerce | Allow all | Traffic volume priority |
| Enterprise Tech | Selective by content type | Protect proprietary, share thought leadership |
Conclusion
AI crawlers now represent 20% of Googlebot’s traffic volume and drive referral traffic that’s up 357% year-over-year. Whether these bots can crawl your website—and which specific ones you allow—directly impacts your brand’s visibility in the AI-powered search experiences your buyers increasingly prefer.
Start with a technical audit: check server logs for AI bot activity, review your robots.txt configuration, and verify your JavaScript rendering approach. Pepper’s Atlas platform automates ongoing monitoring, tracking your brand presence across ChatGPT, Perplexity, and AI Overviews while identifying optimization opportunities based on competitive share-of-voice. This baseline data transforms AI visibility from guesswork into measurable strategy.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the difference between GPTBot and ChatGPT-User?
GPTBot scrapes the web to train OpenAI’s models (improving the brain). ChatGPT-User scrapes the web to answer specific user questions in real-time (browsing).
2. Can AI crawlers read my React/Angular website?
Generally, no. Most AI crawlers cannot execute JavaScript. If your content is rendered client-side, these bots will likely see a blank page. You must use Server-Side Rendering (SSR).
3. Does blocking AI bots hurt my Google SEO?
No. Blocking GPTBot or ClaudeBot does not affect your rankings on Google Search. However, it will prevent you from appearing in AI-generated answers on ChatGPT or Claude.
4. How do I stop AI from training on my content, but still appear in search?
Configure your robots.txt to Disallow: / for GPTBot (training) but Allow: / for ChatGPT-User (search).
5. What is the crawl-to-referral ratio?
This measures how many times a bot hits your server versus how many human visitors it sends back. Perplexity has a healthy ratio (low crawl, high traffic), while Anthropic has a poor one (high crawl, low traffic).


