
On-page SEO (also known as on-site SEO) is the practice of optimizing individual web pages to rank higher in search engines and earn more relevant traffic. It involves aligning page-level elements like content, title tags, HTML source code, and internal links with user search intent.
Unlike Off-Page SEO (which relies on external signals like backlinks), On-Page SEO is 100% within your control.
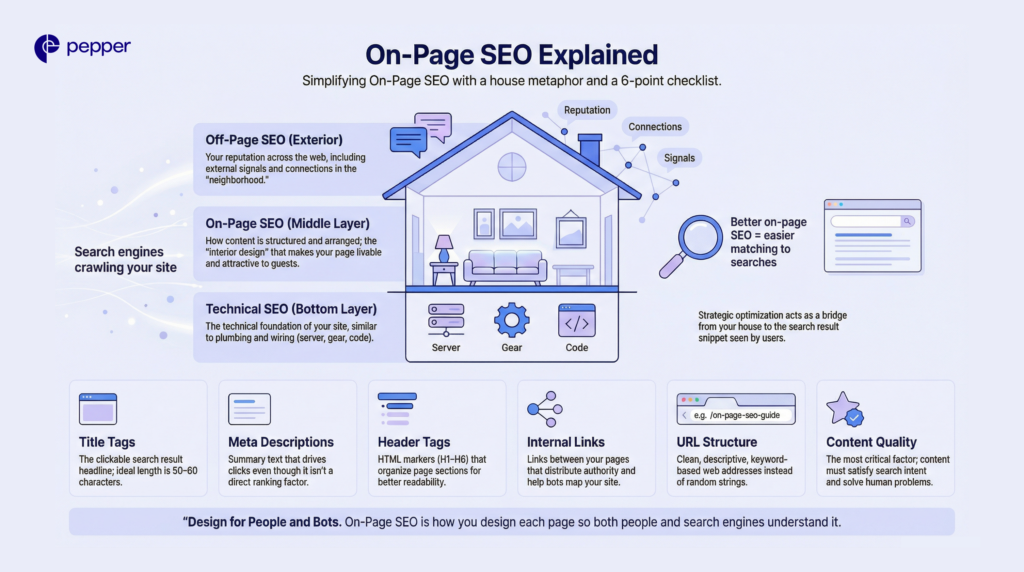
On-Page SEO Explained
Think of your website as a house. Technical SEO is the foundation (plumbing/wiring), Off-Page SEO is your reputation in the neighborhood, and On-Page SEO is the interior design—how you arrange the furniture to make it livable and attractive to guests (Google and users).
Search engines crawl your site to understand what your content covers and who it serves. When you optimize on-page factors, you are speaking Google’s language, making it easier for the algorithm to match your page to specific user queries.
The 6 Core Elements of On-Page SEO
To rank effectively, every page should be optimized for these six pillars:
- Title Tags: The clickable headline in search results. This is a primary ranking factor. (Ideal length: 50–60 characters).
- Meta Descriptions: The summary text beneath the title. While not a direct ranking factor, a compelling description drives Click-Through Rate (CTR).
- Header Tags (H1–H6): HTML markers that structure your content. H1 is your main topic, while H2s and H3s organize subtopics for readability.
- Internal Links: Hyperlinks pointing to other pages on your own site. These transfer authority (PageRank) and help crawlers map your site structure.
- URL Structure: Clean, descriptive web addresses that include your target keyword (e.g.,
/blog/what-is-on-page-seoinstead of/blog/p=123). - Content Quality: The most critical factor. Content must satisfy “Search Intent”—answering the user’s query comprehensively and authoritatively.
Why On-Page SEO Matters
On-page SEO is the difference between content that exists and content that gets found.
- 68% of all online experiences begin with a search engine.
- More than 95% of web pages get zero traffic from Google.
- The #1 result in Google captures 27.6% of all clicks.

| Remember: Without proper on-page signals, even high-quality writing remains invisible because search algorithms cannot contextually understand it. |
What Is Internal Linking in On-Page SEO?
Internal linking is often the most undervalued aspect of on-page strategy. It serves three distinct purposes:
- Navigation: It guides visitors to related content, keeping them on your site longer (reducing bounce rate).
- Crawlability: It creates pathways for Googlebot to find new or deep pages.
- Authority Flow: It distributes “link juice” from your high-performing pages to your new or lower-ranking pages.

Pro Tip: Don’t leave pages as “orphans” (pages with no incoming links). Every page on your site should have at least one internal link pointing to it.
On-Page SEO vs. Off-Page SEO
Both strategies must work together. Strong On-Page SEO creates content worth linking to; Off-Page SEO validates that content with external trust signals.
| Aspect | On-Page SEO | Off-Page SEO |
|---|---|---|
| Control | Fully within your control | Depends on external sources |
| Focus | Content, HTML, site structure | Backlinks, social signals, brand mentions |
| Key Elements | Title tags, meta descriptions, headings, and content | Link building, guest posting, PR |
| Timeline | Immediate changes possible | Requires ongoing relationship building |

| 📌 The “Stick-to-Monitor” Summary If you only remember three things from this guide, make it these: 1. Unlike backlinks (which are like popularity votes), On-Page SEO is entirely in your hands. 2. Write content that solves a human’s problem, then use HTML tags (H1s, Titles) to help the bot understand it. 3. Every page needs internal links pointing to it. No links = no love from Google. |
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is on-page SEO and why is it important?
On-page SEO optimizes webpage elements you control—content, HTML, structure—to improve search rankings. It matters because it determines whether search engines understand and surface your content for relevant queries.
2. What is the role of the meta title in on-page SEO?
The meta title appears as the clickable headline in search results. It signals relevance to search engines and influences whether users click through, making it one of the most impactful on-page elements.
3. How do meta descriptions affect SEO?
Meta descriptions aren’t direct ranking factors, but they influence click-through rates. Higher CTR signals quality to Google, which can indirectly improve rankings over time.
4. What is internal linking and how does it help SEO?
Internal linking connects your website’s pages through hyperlinks. It helps search engines discover content, understand site hierarchy, and distribute ranking value across pages.
5. How often should I update on-page SEO elements?
Review on-page elements quarterly or when content performance declines. Update title tags, meta descriptions, and content when targeting new keywords or refreshing outdated information.


