What Is a 301 Redirect? Meaning & SEO Use Cases

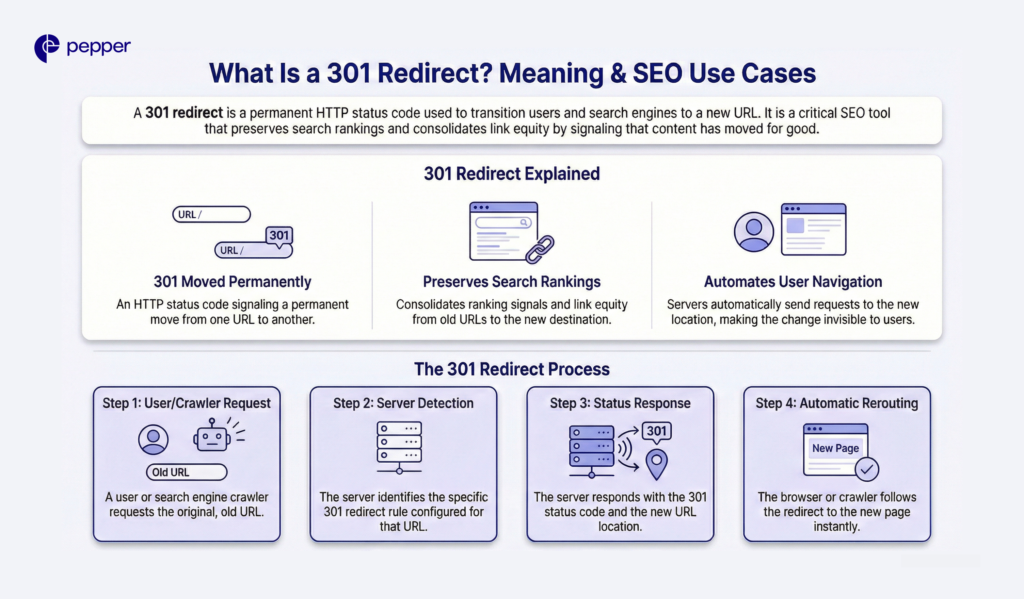
A 301 redirect is an HTTP status code that permanently redirects users and search engines from one URL to another. It signals that content has moved permanently, transferring link equity and preserving search rankings when URLs change.
When someone requests a URL with a 301 redirect configured, the server automatically sends them to the new destination. Search engines update their index to reflect the change, consolidating ranking signals from the old URL to the new one.
301 Redirect Explained
The “301” in 301 redirect refers to the HTTP status code, officially named “301 Moved Permanently.” When your server returns this code, it tells browsers and search engine crawlers that the original URL no longer exists and all future requests should go to the new location.
Here’s what happens technically:
- A user or crawler requests the old URL
- The server detects the 301 redirect rule
- The server responds with the 301 status code and the new URL location
- The browser or crawler automatically follows the redirect to the new page
This process happens in milliseconds, invisible to most users.
Why 301 Redirects Matter for SEO
301 redirects preserve the SEO value you’ve built over time. When you change a URL without redirecting it, you lose all accumulated link equity, rankings, and traffic to that page.
Google transfers authority, ranking power, and backlinks from the old URL to the new location when encountering a 301 redirect.
Common scenarios requiring 301 redirects:
- Domain changes: Rebranding from oldcompany.com to newcompany.com
- HTTPS migration: Moving from HTTP to HTTPS
- URL structure updates: Changing /blog/post-title to /resources/post-title
- Content consolidation: Merging duplicate pages into one authoritative version
- Deleted pages: Redirecting removed content to relevant alternatives

301 vs 302 Redirect: What’s the Difference?
| Aspect | 301 Redirect | 302 Redirect |
|---|---|---|
| Signal | Permanent move | Temporary move |
| Link equity | Transfers to new URL | Stays with original URL |
| Search index | New URL replaces old | Original URL remains indexed |
| Use case | Site migrations, deleted pages | A/B testing, maintenance pages |
The key distinction: 301 redirects tell search engines to transfer all SEO value to the new URL and remove the old one from their index. 302 redirects keep the original URL indexed because the change is temporary.
Using a 302 when you mean 301 is a common mistake. Search engines won’t transfer link equity, and your new URL won’t inherit the ranking power from the original.

| Quick Takeaway: Use 301 redirects for permanent URL changes to preserve SEO value, and 302 redirects only for genuinely temporary moves like A/B tests or scheduled maintenance. |
Frequently Asked Questions
What does a 301 redirect mean in simple terms?
A 301 redirect automatically sends visitors from an old web address to a new one, telling search engines the move is permanent and to transfer all ranking value to the new location.
Do 301 redirects pass link equity?
Yes. Since 2016, Google has confirmed that 301 redirects pass full link equity to the destination URL, preserving the SEO value accumulated by the original page.
When should a 301 redirect be used?
Use 301 redirects for permanent changes: domain migrations, HTTPS upgrades, URL restructuring, content consolidation, and redirecting deleted pages to relevant alternatives.
How long do 301 redirects take to process?
Search engines typically consolidate the old and new URLs within days to months, depending on crawl frequency. Keep 301 redirects active for at least one year to ensure a complete transition.
Can too many 301 redirects hurt SEO?
Individual 301 redirects don’t harm SEO, but redirect chains (multiple redirects in sequence) slow page speed and waste crawl budget. Aim for direct redirects to final destinations.


