What Is Crawling in SEO? How Search Engines Discover Your Pages

Crawling is the technical process where search engine bots (known as spiders or crawlers) systematically browse the internet to discover, scan, and download web page content.
Before your website can appear in search results (ranking), it must be stored in a database (indexing). However, before it can be indexed, it must be found. That first step is crawling.
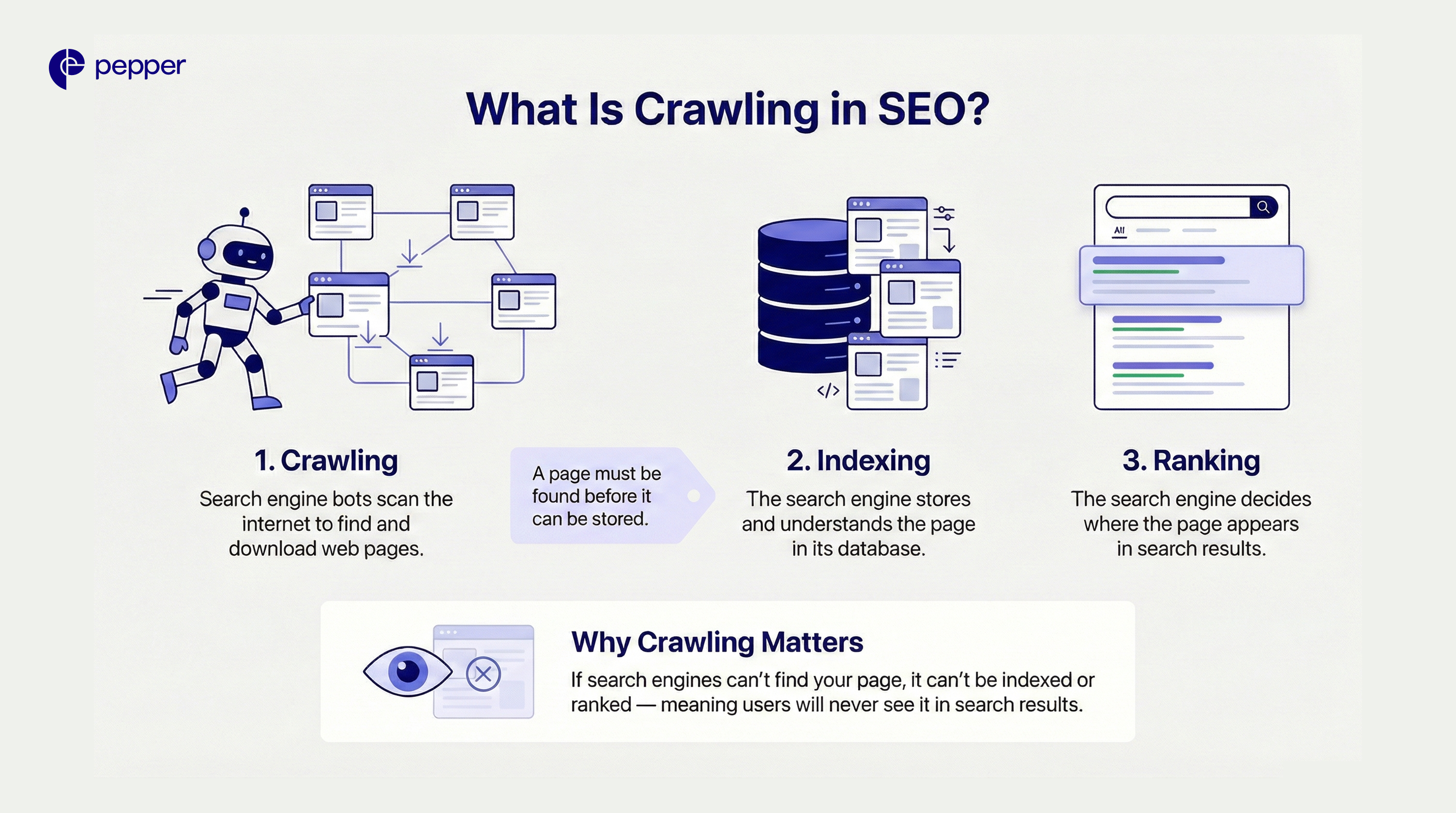
How Search Engine Crawlers Work
Think of crawlers as digital librarians constantly scanning for new books. The process follows a specific cycle:
- Seed URLs: The crawler starts with a known list of web addresses.
- Link Discovery: It visits those pages and identifies every hyperlink (internal and external) on the page.
- The Queue: These newly discovered links are added to the “Crawl Frontier” (a to-do list).
- Download: The bot visits the pages in the queue, downloads the HTML, text, images, and JavaScript, and passes them to the indexing processor.
Common Web Crawlers
Different search engines use proprietary bots:
- Google: Googlebot
- Bing: Bingbot
- Yandex: Yandex Bot
- Baidu: Baiduspider
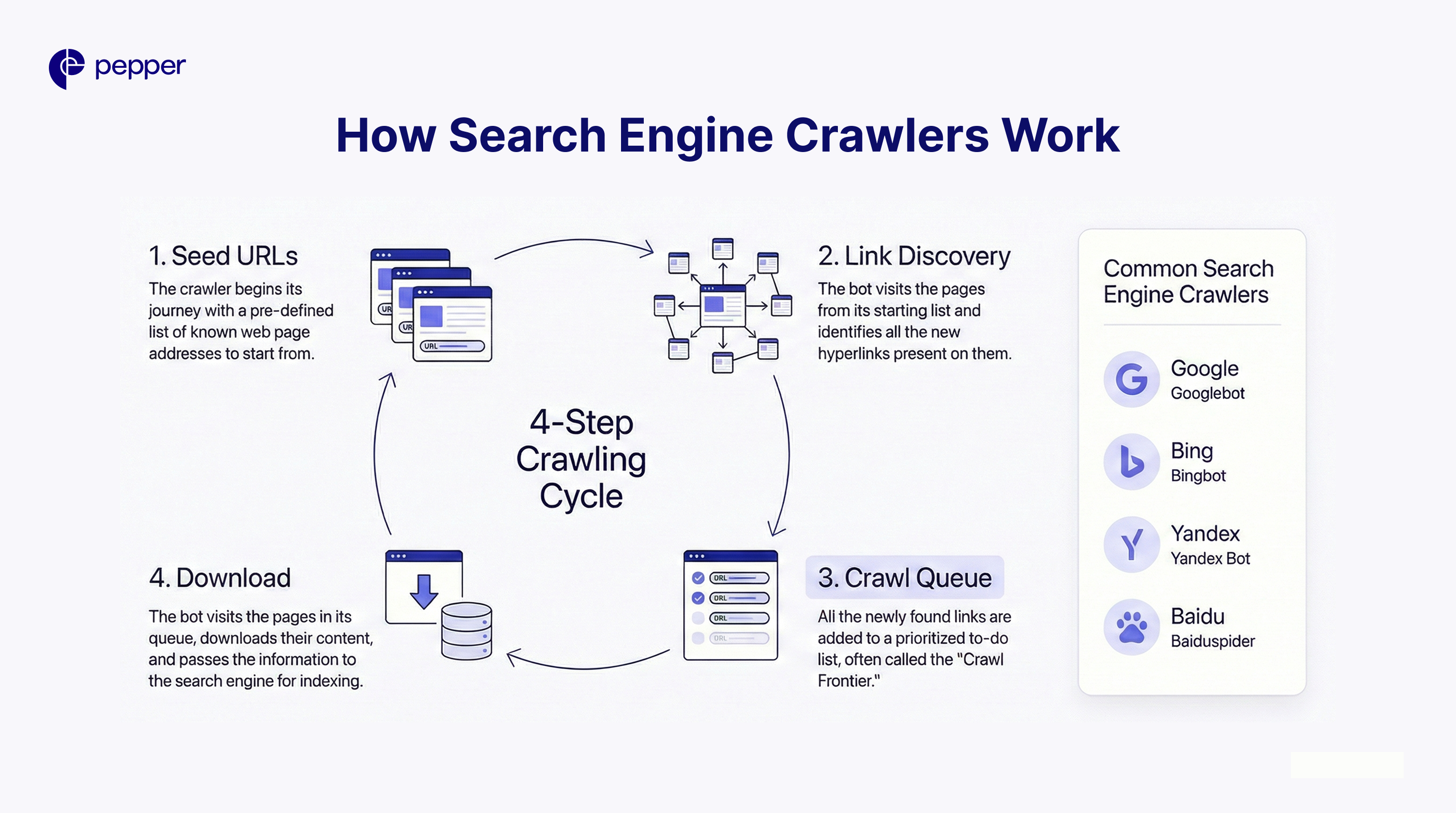
Crawling vs. Indexing vs. Ranking
It is vital to understand that being crawled does not guarantee ranking.
| Stage | Action | Goal |
| 1. Crawling | The bot visits and downloads the page. | Discovery and Accessibility |
| 2. Indexing | Search engine analyzes and stores content. | Storage and Understanding |
| 3. Ranking | The algorithm positions the page for queries. | Authority and Relevance |
Tracking Visibility Beyond Rankings: Once your pages are crawled and indexed, the game isn’t over. Modern SEO requires tracking how your brand appears in AI-generated answers (like Google’s AI Overviews).
Pepper’s Atlas is the first tool to measure this “Generative Engine Optimization” (GEO), helping you see not just if you rank, but how AI search engines are citing your content.
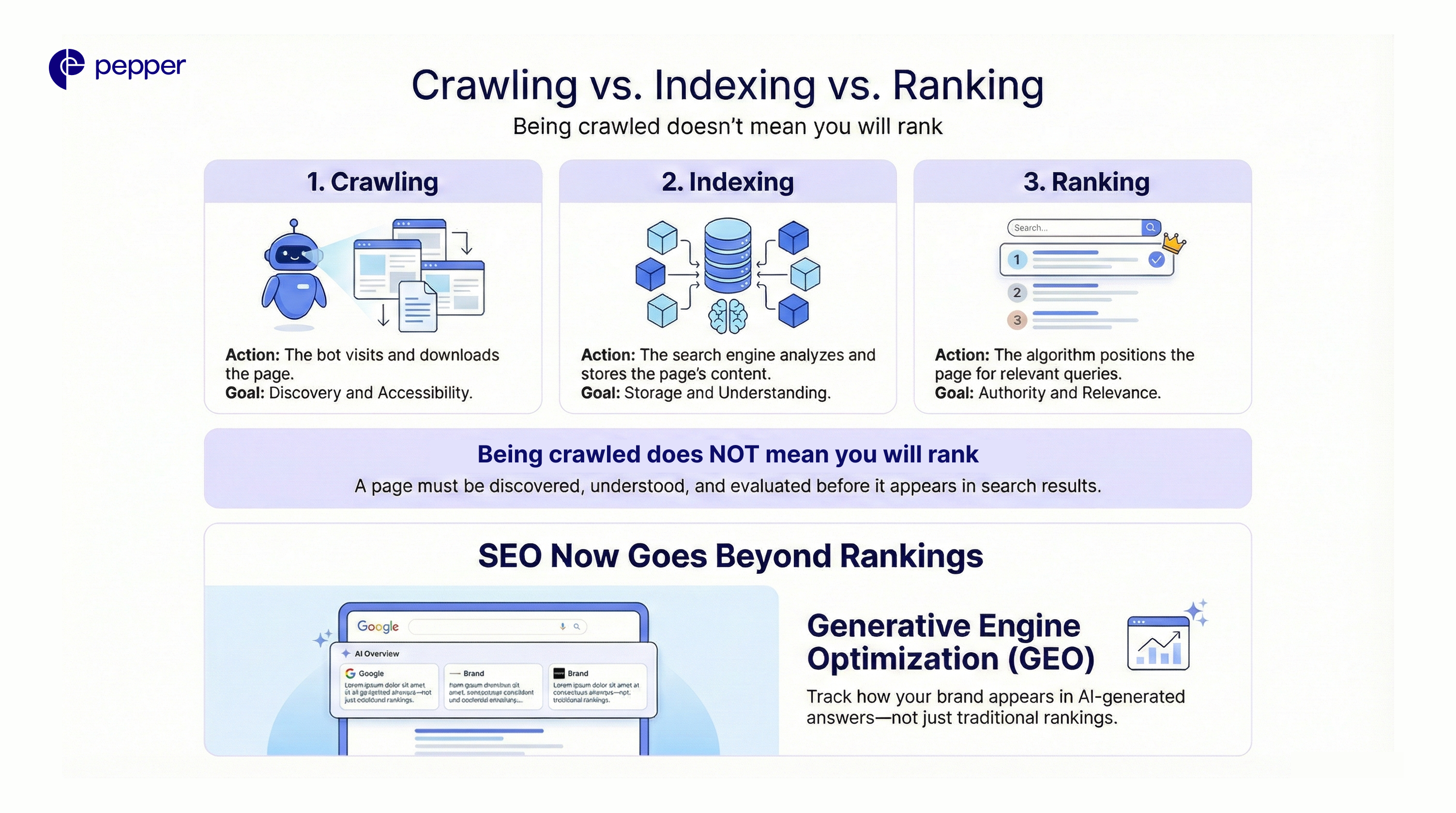
How to Optimize Your Site for Crawling
To ensure Googlebot finds your content quickly, focus on these five areas:
1. Optimize Your Robots.txt
This file acts as the “gatekeeper.” It tells bots which parts of your site not to visit.
- Common Error: Accidentally disallowing the whole site (
Disallow: /). - Best Practice: Only block low-value pages (admin pages, shopping carts) to save crawl resources.
2. Use XML Sitemaps
An XML sitemap is a roadmap you submit directly to Google Search Console. It lists all the URLs you want crawled, bypassing the need for the bot to find them via links naturally.
3. Strengthen Internal Linking
Crawlers navigate via links. If a page has no internal links pointing to it (an “Orphan Page”), crawlers may never find it. Ensure high-priority pages are linked from your homepage or main navigation.
4. Improve Server Response Time
If your server is slow (5xx errors) or times out, Googlebot will limit its activity to prevent crashing your site. A faster site allows for a deeper crawl.
5. Manage “Crawl Budget” (For Large Sites)
Crawl budget is the number of pages Google is willing to crawl on your site daily.
- Small Sites (<1k pages): Rarely need to worry about this.
- Large Sites (10k+ pages): Must optimize by removing duplicate content, redirect chains, and low-quality URLs to ensure the budget is spent on important pages.
| Key Takeaways: 1. Crawling is the Foundation: It is the discovery process where bots find and download your content; without it, indexing and ranking are impossible. 2. The SEO Hierarchy: Remember the sequence—a page must be crawled to be indexed, and it must be indexed to appear in search results. 3. Navigation Matters: Search bots rely heavily on XML sitemaps and internal links to find deep pages and understand site structure. 4. Technical Health is Critical: Slow server speeds, broken links, or robots.txt errors can block crawlers and waste your site’s crawl budget. |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is crawling in SEO?
Crawling is the discovery phase where search engine bots scan websites to download content (text, images, code). It is the prerequisite to indexing and ranking.
2. How often does Google crawl a website?
There is no set schedule. High-authority news sites may be crawled every few minutes, while smaller, static websites might be crawled every few weeks. You can check your specific stats in Google Search Console.
3. What stops a bot from crawling a site?
Common blockers include server errors (500s), incorrect robots.txt rules, password protection, and “noindex” tags.
4. Does social media affect crawling?
Indirectly. While social links are usually “nofollow,” sharing content on social media drives traffic. If that traffic leads to external sites linking to you, crawlers will find your site faster.
5. How do I request a crawl?
You can force a crawl for a single page by using the “URL Inspection Tool” in Google Search Console and clicking “Request Indexing.”
Get your hands on the latest news!
Similar Posts

Content Analytics
8 mins read
Google I/O 2025: AI Search Shake-Up & Ranking Volatility

SEO
5 mins read
Top 10 Agencies for Banking and Financial SEO Services Industry

SEO
4 mins read