What is Indexing? How Google Stores Your Web Pages
Indexing is the process by which Google analyzes, categorizes, and stores web pages in its massive database so they can appear in search results. If Google doesn’t index your page, it won’t rank anywhere—not on page one or page 1,000.
Indexing Explained
Think of Google’s index like the index at the back of a book. It contains an entry for every word seen on every webpage Google has stored. The Google Search index contains hundreds of billions of webpages and exceeds 100,000,000 gigabytes in size.
During indexing, Google processes your page’s text, images, videos, title tags, and alt attributes. The search engine determines what your page covers and whether it offers unique value compared to similar content already indexed.
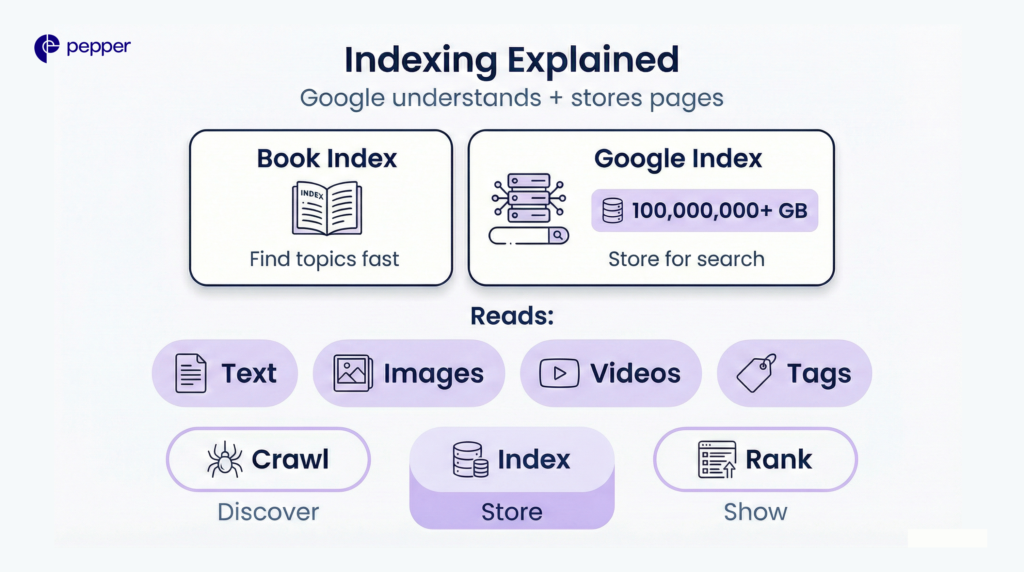
Remember: Indexing follows crawling but precedes ranking. Googlebot first discovers and fetches your page (crawling), then Google analyzes and stores it (indexing), and finally, algorithms determine where it appears in search results (ranking).
Why Indexing Matters
Without proper indexing, your SEO efforts produce zero results. Your carefully optimized content remains invisible to searchers.
For B2B marketers, indexing failures mean lost organic traffic opportunities. Your product pages, blog posts, and landing pages can’t generate leads if Google never stores them.
How Google Indexing Works
Google’s indexing process involves several technical steps:
- Content Analysis: Googlebot parses your HTML code, breaking it into elements, tags, attributes, and text content. If semantic errors exist, Google automatically corrects them.
- Duplicate Detection: Google identifies whether your page duplicates content from other indexed pages. When duplicates exist, Google clusters similar pages and selects one canonical version to display in results.
- Storage: Information about canonical pages and their clusters gets stored across thousands of computers in Google’s data centers.

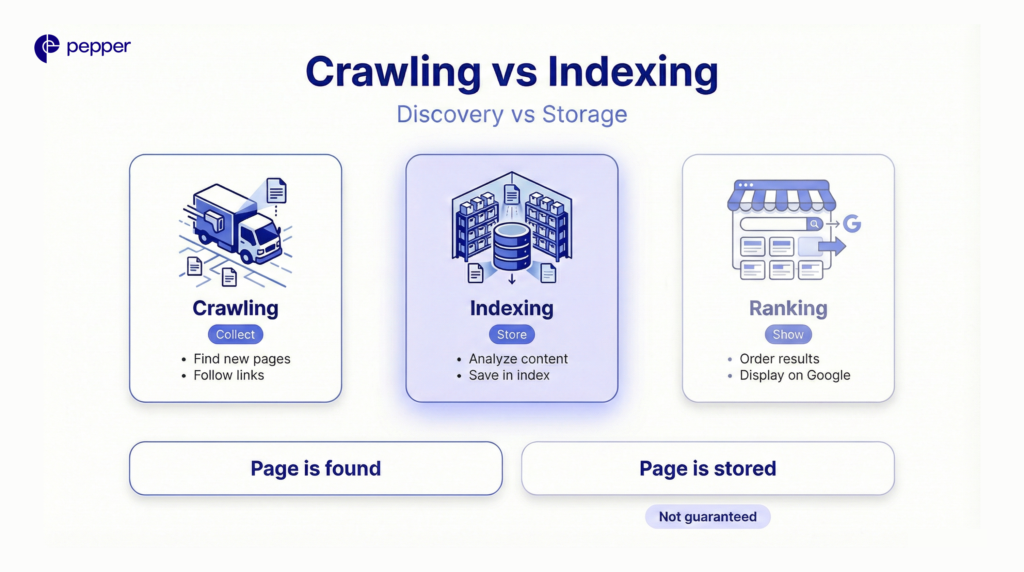
Crawling SEO vs Google Indexing
| Aspect | Crawling | Indexing |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Discover new and updated pages | Analyze and store page content |
| Process | Googlebot follows links across the web | Google processes text, images, and media |
| Outcome | Page is found | Page enters Google’s database |
| Guarantee | Happens automatically via links | Not guaranteed—quality matters |
What Does the Status “Crawled Currently Not Indexed” Mean in Google Search Console?
The “crawled currently not indexed” status in Google Search Console means Google visited your page but decided against adding it to the index. This typically indicates quality concerns.
Common causes include thin content, duplicate material, or site-wide quality issues. Google’s John Mueller recommends improving overall site structure and content quality rather than fixing individual pages.

| Key Takeaways: Indexing determines whether your pages can appear in Google search results.Focus on content quality, uniqueness, and proper technical setup to ensure Google stores your pages in the Google search index.Pepper’s Atlas platform tracks brand visibility across both traditional search indexes and AI-generated answers, helping you understand where your content appears after Google processes it. |
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the difference between crawling and indexing?
Crawling is when Googlebot discovers and fetches your page. Indexing is when Google analyzes that page and stores it in its database for search results.
2. How long does it take to index a website on Google?
Indexing timeframes vary from days to weeks, depending on site authority, crawl budget, and content quality. New sites typically take longer than established domains.
3. Why is my page crawled but not indexed?
Google may view your content as low-quality, duplicate, or lacking unique value. Improving content depth and site-wide quality often resolves this status.
4. How can I check if Google indexed my page?
Use Google Search Console’s URL Inspection tool or search “site:yoururl.com” in Google to verify indexing status.
5. Does submitting a sitemap guarantee indexing?
No. Sitemaps help Google discover URLs faster, but indexing decisions depend on content quality and uniqueness, not sitemap submission.