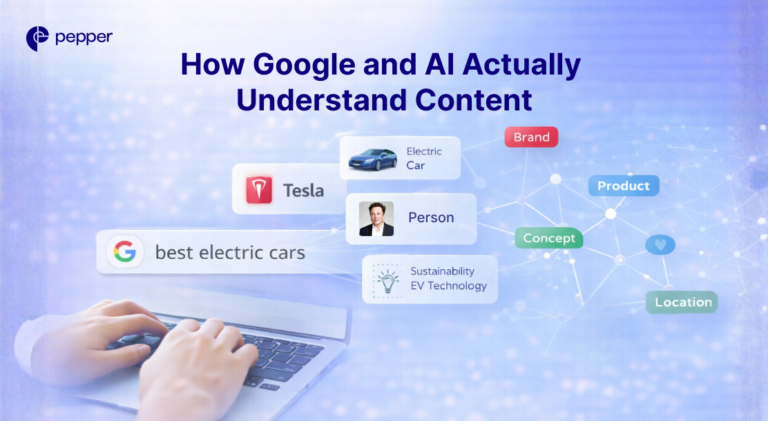
What Is Internal Linking? Meaning and SEO Best Practices

Internal linking is the practice of connecting one page on your website to another page on the same domain using hyperlinks. These links help search engines understand your site structure, distribute page authority, and guide users to related content—making them foundational to both SEO and user experience.
Internal Linking Explained
Internal links work like signposts within your website. When you link from one page to another on the same domain, you create pathways for both visitors and search engine crawlers to discover related content.
Every internal link passes link equity (sometimes called “link juice”)—the SEO value that flows from one page to another. Your homepage typically carries the highest authority because it earns the most external backlinks. When you link from high-authority pages to newer or less visible content, that SEO strength transfers, helping those pages rank better.
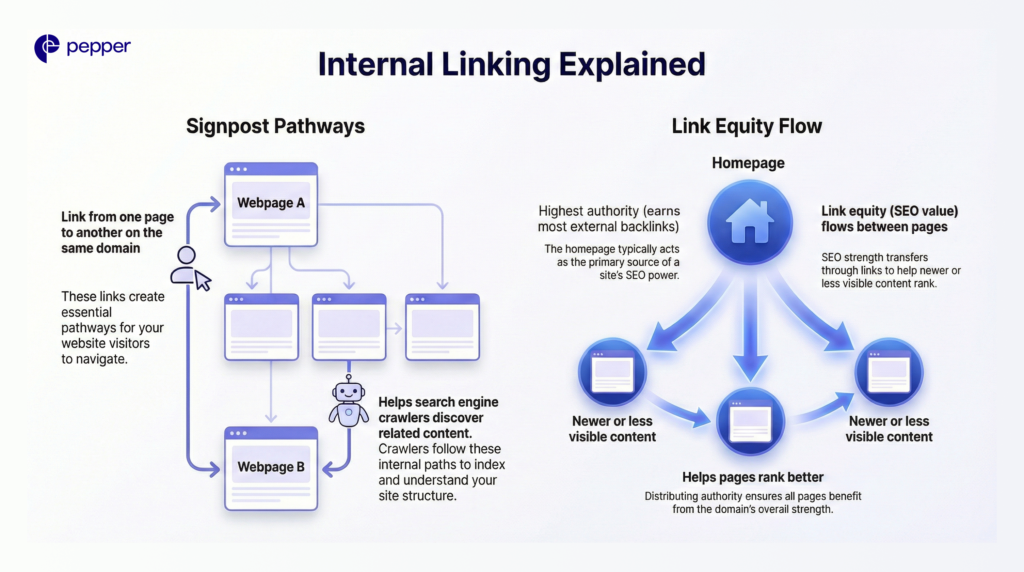
| Remember: Search engines follow internal links to crawl, index, and understand how your pages relate to each other. A well-connected page signals importance, while pages with few or no internal links (called “orphan pages”) struggle to get indexed and ranked. |
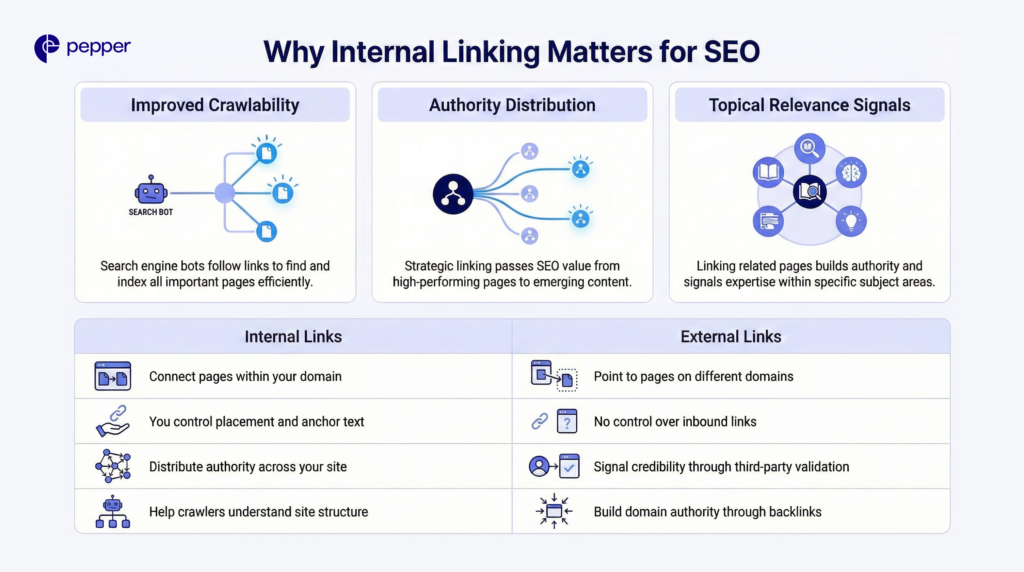
Why Internal Linking Matters for SEO
Internal links deliver three core benefits for search performance.
- Improved crawlability: Search engine bots discover new content by following links. Strong internal linking ensures all important pages get found and indexed efficiently.
- Authority distribution: Strategic linking passes SEO value from high-performing pages to those needing a ranking boost. This helps emerging content compete faster.
- Topical relevance signals: When related pages link to each other, search engines understand your content clusters and topical expertise. This builds authority within specific subject areas.
| Internal Links | External Links |
|---|---|
| Connect pages within your domain | Point to pages on different domains |
| You control placement and anchor text | No control over inbound links |
| Distribute authority across your site | Signal credibility through third-party validation |
| Help crawlers understand site structure | Build domain authority through backlinks |
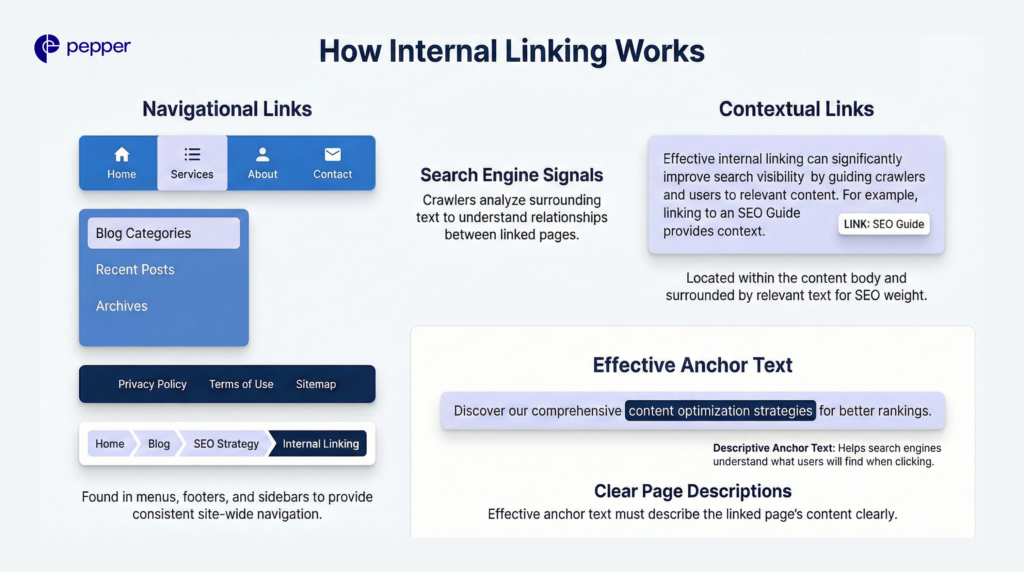
How Internal Linking Works
Two primary types of internal links serve different purposes.
- Navigational links appear in menus, footers, sidebars, and breadcrumbs. These provide consistent site-wide navigation but offer limited contextual signals to search engines.
- Contextual links sit within your content body, surrounded by relevant text. These carry more SEO weight because crawlers can analyze the surrounding context to understand the relationship between pages.
| Did You Know? The three-click rule suggests that any page should be reachable within three clicks from your homepage. Pages buried deeper in your site structure typically receive less authority and generate significantly less organic traffic. |
Effective anchor text describes the linked page’s content clearly. For example, linking the phrase “content optimization strategies” to a page about that topic helps search engines understand what users will find when they click.
Internal Linking Best Practices
- Link from high-authority pages: Identify your strongest pages (those with the most backlinks or traffic) and add links from them to newer content that needs visibility.
- Use descriptive anchor text: Avoid generic phrases like “click here.” Instead, use natural, keyword-relevant phrases that describe the destination page.
- Maintain reasonable link density: Aim for 5-10 internal links per 2,000 words of content. Excessive linking can dilute value and trigger search engine penalties similar to keyword stuffing.
- Fix orphan pages: Audit regularly for pages with zero internal links pointing to them. These pages are effectively invisible to search engines and users navigating your site.
- Create topic clusters: Group related content around pillar pages, linking supporting articles back to the main resource. This structure signals topical depth and authority.

| Quick Takeaway: Internal linking helps search engines crawl your site, distributes page authority where you need it, and guides users to relevant content—making it one of the highest-impact SEO tactics fully within your control. |
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How many internal links should a page have?
Aim for 5-10 internal links per 2,000 words, or roughly one link every 200-300 words. Avoid excessive linking, as search engines may devalue pages that appear to manipulate link structure.
2. What’s the difference between internal and external links?
Internal links connect pages within the same website domain. External links point to pages on different websites, signaling credibility through third-party references.
3. How do internal links affect page authority?
Internal links pass link equity from the source page to the destination. Linking from high-authority pages to newer content transfers SEO value, helping those pages rank faster.
4. What are orphan pages and why do they matter?
Orphan pages have no internal links pointing to them, making them difficult for search engines and users to discover. These pages typically perform poorly in search results.
5. Should internal link anchor text include keywords?
Yes, use descriptive anchor text that naturally incorporates relevant keywords. This helps search engines understand what the linked page covers without appearing manipulative.